The Vital Role of UK Emergency Medicine Experts in Handling Acute Psychiatric Emergencies
The Growing Need for Psychiatric Emergency Care
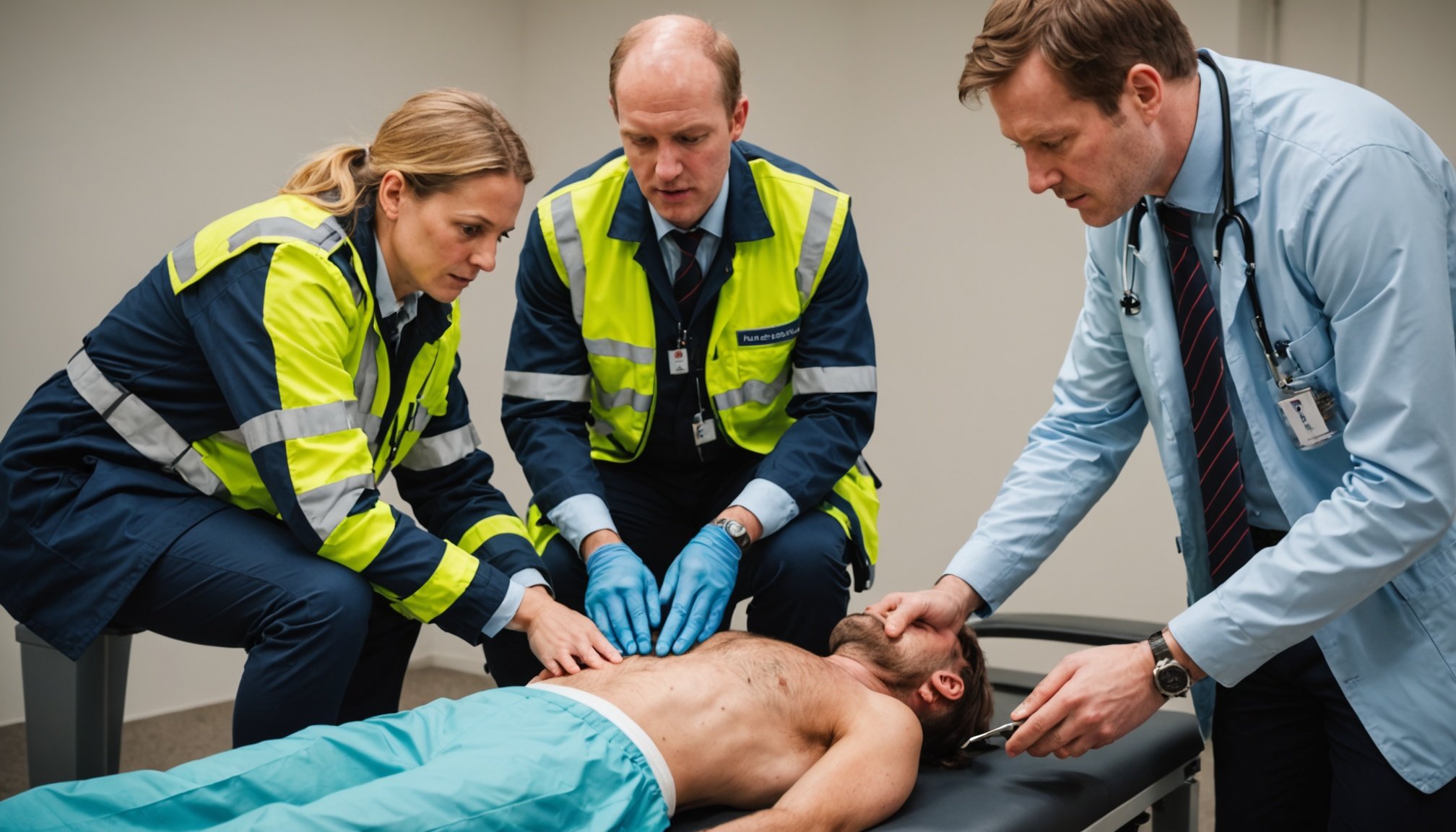
In the United Kingdom, the demand for psychiatric emergency care has been on the rise, highlighting the critical role that emergency medicine experts play in managing acute mental health crises. The Royal College of Emergency Medicine (RCEM) has consistently emphasized the importance of timely and effective emergency care, especially in the context of mental health presentations.
“Mental health crises are just as urgent as physical health emergencies,” notes Dr. James Gagg, South West Regional Chair of the RCEM. “The ability to provide immediate and compassionate care is crucial in these situations.”
Have you seen this : Top Strategies for UK Plastic Surgeons in Mastectomy Reconstructive Surgery: Best Practices Revealed
The Challenges Faced by Emergency Departments
Emergency departments across the UK are often overwhelmed with patients presenting with a range of health issues, including acute psychiatric emergencies. Long wait times, overcrowding, and a lack of social care options exacerbate these challenges.
“Emergency Department crowding represents the greatest threat to the timely delivery of emergency care in the UK and across the world,” warns the RCEM. This crowding can lead to delays in mental and physical assessments, increasing the risk of adverse outcomes for mental health patients.
Topic to read : Essential Protocols for UK Occupational Therapists to Enhance Fine Motor Skill Recovery in Adults After a Stroke
Initial Assessment and Triage
When patients present to the emergency department with psychiatric emergencies, the initial assessment is paramount. This process involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s mental and physical health.
Key Components of Initial Assessment:
- Mental Health Screening: Identifying symptoms of mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or psychosis.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the risk of self-harm or harm to others.
- Physical Health Assessment: Checking for any underlying physical health issues that may be contributing to the psychiatric presentation.
- Social and Environmental Factors: Assessing the patient’s social support network and living situation.
For example, at St Peter’s Hospital in Chertsey, the emergency department has a dedicated team that includes a counselling service and a trauma team, which are essential for providing a holistic initial assessment.
The Role of Emergency Medicine Experts
Emergency medicine experts are at the forefront of managing acute psychiatric emergencies. These professionals must be equipped with the skills to handle both the clinical and psychological aspects of patient care.
Skills and Training:
- Clinical Competence: The ability to diagnose and treat a wide range of psychiatric conditions.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication with patients, families, and other healthcare providers.
- Crisis Management: Training in de-escalation techniques and crisis intervention.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Working closely with mental health teams, social services, and community health providers.
The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) offers workshops and training programs, such as the “Doctors as Leaders: Organisational Leadership” workshop, which helps doctors develop the leadership skills necessary to manage complex healthcare environments, including those involving psychiatric emergencies.
Liaison Mental Health Services
Liaison mental health services are crucial in bridging the gap between emergency departments and community mental health services. These services ensure that patients receive continuous care beyond their initial emergency visit.
Benefits of Liaison Services:
- Continuity of Care: Ensuring that patients have access to ongoing mental health support.
- Reduced Readmissions: By providing community-based care, liaison services can reduce the likelihood of patients returning to the emergency department.
- Improved Outcomes: Tailored treatment plans that address both mental and physical health needs.
For instance, the RCEM has advocated for stronger collaboration between emergency departments and community mental health services to reduce wait times and improve patient outcomes.
Community Mental Health Integration
Integrating emergency care with community mental health services is essential for providing comprehensive care to patients.
Strategies for Integration:
- Early Intervention Teams: Teams that provide early intervention and support to patients in the community.
- Crisis Resolution Teams: Teams that offer intensive, short-term support to patients in crisis.
- Community Outreach: Outreach programs that bring mental health services directly to patients in their communities.
The UK-Med, a WHO-verified Emergency Medical Team, also emphasizes the importance of community integration in their global humanitarian responses, highlighting the universal need for cohesive health systems.
Practical Insights and Actionable Advice
For those working in emergency medicine, here are some practical insights and actionable advice for handling acute psychiatric emergencies:
Tips for Healthcare Providers:
- Stay Calm and Empathetic: Maintaining a calm and empathetic demeanor can help de-escalate crises.
- Use Clear Communication: Clear and simple communication can help patients understand their treatment plans.
- Involve Family and Friends: Involving family and friends in the care process can provide additional support and insight.
- Follow-Up Care: Ensuring that patients have follow-up appointments and access to community resources is crucial for ongoing care.
Advice for Patients and Families:
- Seek Help Early: Early intervention can prevent crises from escalating.
- Know Your Resources: Being aware of local mental health resources and emergency services can be lifesaving.
- Communicate Openly: Open communication with healthcare providers about mental health concerns is essential.
The role of UK emergency medicine experts in handling acute psychiatric emergencies is multifaceted and critical. From initial assessment and triage to liaison mental health services and community integration, these professionals are at the forefront of providing compassionate and effective care.
As the health care system continues to evolve, it is clear that the need for skilled emergency medicine experts will only grow. By understanding the challenges, the importance of comprehensive training, and the benefits of integrated care, we can work towards a healthcare system that better serves all patients, including those in mental health crises.
Table: Comparison of Emergency Department and Community Mental Health Services
| Service | Emergency Department | Community Mental Health Services |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Immediate stabilization and treatment | Ongoing care and support |
| Setting | Hospital-based | Community-based |
| Staff | Emergency medicine doctors, nurses, and support staff | Mental health professionals, social workers, and community outreach workers |
| Interventions | Crisis intervention, medication management, physical health assessment | Therapy, counseling, support groups, and community outreach |
| Goals | Stabilize the patient, address immediate health concerns | Provide long-term support, prevent future crises |
| Access | 24/7 access | Scheduled appointments and outreach services |
Detailed Bullet Point List: Key Steps in Managing Acute Psychiatric Emergencies
-
Initial Triage:
-
Rapid assessment of the patient’s mental and physical state.
-
Prioritization based on the severity of the condition.
-
Comprehensive Assessment:
-
Detailed mental health screening.
-
Physical health examination.
-
Social and environmental assessment.
-
Crisis Intervention:
-
De-escalation techniques.
-
Medication management.
-
Involvement of family and friends.
-
Treatment Planning:
-
Development of a tailored treatment plan.
-
Coordination with mental health services.
-
Arrangement for follow-up care.
-
Liaison with Community Services:
-
Referral to community mental health services.
-
Collaboration with social services.
-
Ensuring continuity of care.
-
Follow-Up Care:
-
Scheduling follow-up appointments.
-
Providing patients with resources and support.
-
Monitoring patient progress and adjusting treatment plans as necessary.
By understanding and addressing the complexities of acute psychiatric emergencies, we can improve the care and outcomes for these vulnerable patients, ensuring that they receive the compassionate and effective treatment they deserve.